Category Archives: healthy habits
Blue Zones: Terraformers…
Blue Zones employs evidence-based ways to help people live longer, better. The Company’s work is rooted in the New York Times best-selling books The Blue Zones and Thrive—both published by National Geographic books. In 2009, Blue Zones applied the tenets of the books to Albert Lea, MN and successfully raised life expectancy and lowered health care costs for city workers by 40%. Blue Zones takes a systematic, environmental approach to well-being which focuses on optimizing policy, building design, social networks, and the built environment. The Blue Zones Project is based on this innovative approach.
Dementia Researchers Call for G-8 to Focus on Prevention
- 44 million people have dementia worldwide
- better diet, exercise, low blood pressure, not smoking and avoiding obesity present key aspects of preventing dementia
- Vitamins B6 and B12 and folic acid would cost pennies a day and slowed atrophy of gray matter in brain areas affected by Alzheimer’s disease, according to a study published in May by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Dementia Researchers Call for G-8 to Focus on Prevention
“About half of Alzheimer’s disease cases worldwide might be attributable to known risk factors,” they said in a statement before a G-8 meeting in London tomorrow to coordinate responses to the condition. “Taking immediate action on the known risk factors could perhaps prevent up to one-fifth of predicted new cases by 2025.”
The costs of dementia were estimated at $604 billion for 2010, the group said, and the number of cases is set to more than triple by 2050. The 111 signatories from 36 countries called on governments to back more research into prevention, and policies such as promotion of healthier diets. The G-8 are the U.K., U.S., Germany, France, Canada, Italy, Russiaand Japan.
“The choice is stark,” said Zaven Khachaturian, a signatory and editor-in-chief of U.S. journalAlzheimer’s & Dementia. “Either you invest money in creating this infrastructure for preventing or delaying dementia, or continue along the way. If we continue with the current trends, no country’s health-care system will be able to provide care.”
Cheap Vitamins
Alzheimer’s Disease International estimates that 44 million people worldwide have dementia, which will rise to 76 million in 2030 and 135 million by 2050, according to data from the group of Alzheimer’s associations.
About $40 billion has been invested in drug development efforts that haven’t produced effective new medicines, the researchers said in today’s statement. Even so, recent research suggests there may be cheap options to help tackle the problem.
A cocktail of vitamins B6 and B12 and folic acid would cost pennies a day and slowed atrophy of gray matter in brain areas affected by Alzheimer’s disease, according to a study published in May by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
About half the fall in deaths from conditions such as heart disease and stroke in the past 50 years resulted from modifying risk factors, according to the scientists advocating prevention. Taking a similar approach to dementia by encouraging middle-aged people to adopt healthy lifestyles may ward off the condition as it does other diseases and save “huge sums,” they said.
Healthy Lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle includes exercising; not smoking; following a diet rich in fruit, vegetables and fish; avoiding obesity, diabetes and excessive alcohol; and treating high blood pressure, the researchers said.
Other research is helping to identify people at risk. A person’s chance of getting dementia before age 65 may develop as early as adolescence, according to a study that suggests teens with high blood pressure or who drink excessively are at risk.
Other risk factors include stroke, use of antipsychotics, father’s dementia, drug intoxication, as well as short stature and low cognitive function, according to the study of Swedish men published by the journal JAMA Internal Medicine in August.
G-8 governments should set goals, stimulate more collaborative research, coordinate policies and establish consistent rules for data sharing, intellectual property and ethics, Khachaturian said in a telephone interview.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration hasn’t cleared new drugs for memory loss conditions in a decade. Approved medicines such as Eisai Co. (4523)’s Aricept ease symptoms without slowing or curing dementia.
Useful Lessons
A joint U.S.-European Union task force in 2011 found that all disease-modifying treatments for Alzheimer’s in the previous decade failed late-stage trials “despite enormous financial and scientific efforts.” Since then, at least four more experimental treatments have failed.
Eric Karran, director of research at the charity Alzheimer’s Research UK, who wasn’t among the signatories to the statement, said that failed trials can provide useful lessons. One of the four medicines, Eli Lilly & Co. (LLY)’s solanezumab, is undergoing further tests to determine if it helps people with mild Alzheimer’s disease, Karran said.
“If we could just get efficacy in one approach, we will unlock so much else, we will get so much more understanding,” Karran said at a press conference on Dec. 4. “If solanezumab is shown to work in mild Alzheimer’s disease, the pathway will be to take that earlier and earlier.”
Hammerbacher, Sinai and Minerva…
Top piece on Sinai’s vision. Everything’s lined up there except the doctors – hmmm…. They’ll need some amazing insights to bust through the inertia, but expect they’ll glean them…
In The Hospital Of The Future, Big Data Is One Of Your Doctors
December 5, 2013 | 7:30 AM
From our genomes to Jawbones, the amount of data about health is exploding. Bringing on top Silicon Valley talent, one NYC hospital is preparing for a future where it can analyze and predict its patients’ health needs–and maybe change our understanding of disease.
The office of Jeff Hammerbacher at Mount Sinai’s Icahn School of Medicine sits in the middle of one of the most stark economic divides in the nation. To Hammerbacher’s south are New York City’s posh Upper East Side townhouses. To the north, the barrios of East Harlem.
What’s below is most interesting: Minerva, a humming supercomputer installed last year that’s named after the Roman goddess of wisdom and medicine.
It’s rare to find a supercomputer in a hospital, even a major research center and medical school like Mount Sinai. But it’s also rare to find people like Hammerbacher, a sort of human supercomputer who is best known for launching Facebook’s data science teamand, later, co-founding Cloudera, a top Silicon Valley “big data” software company where he is chief scientist today. After moving to New York this year to dive into a new role as a researcher at Sinai’s medical school, he is setting up a second powerful computing cluster based on Cloudera’s software (it’s called Demeter) and building tools to better store, process, mine, and build data models. “They generate a pretty good amount of data,” he says of the hospital’s existing electronic medical record system and its data warehouse that stored 300 million new “events” last year. “But I would say they are only scratching the surface.”
Combined, the circumstances make for one of the most interesting experiments happening in hospitals right now–one that gives a peek into the future of health care in a world where the amount of data about our own health, from our genomes to ourJawbone tracking devices, is exploding.
“What we’re trying to build is a learning health care system,” says Joel Dudley, director of biomedical informatics for the medical school. “We first need to collect the data on a large population of people and connect that to outcomes.”
To imagine what the hospital of the future could look like at Mount Sinai, picture how companies like Netflix and Amazon and even Facebook work today. These companies gather data about their users, and then run that data through predictive models and recommendation systems they’ve developed–usually taking into account a person’s past history, maybe his or her history in other places on the web, and the history of “similar” users–to make a best guess about the future–to suggest what a person wants to buy or see, or what advertisement might entice them.
Through real-time data mining on a large scale–on massive computers like Minerva–hospitals could eventually operate in similar ways, both to improve health outcomes for individual patients who enter Mount Sinai’s doors as well as to make new discoveries about how to diagnose, treat, and prevent diseases at a broader, public health scale. “It’s almost like the Hadron Collider approach,” Dudley says. “Let’s throw in everything we think we know about biology and let’s just look at the raw measurements of how these things are moving within a large population. Eventually the data will tell us how biology is wired up.”
Dudley glances at his screen to show the very early inklings of this vision of what “big data” brought to the world of health care and medical research could mean.
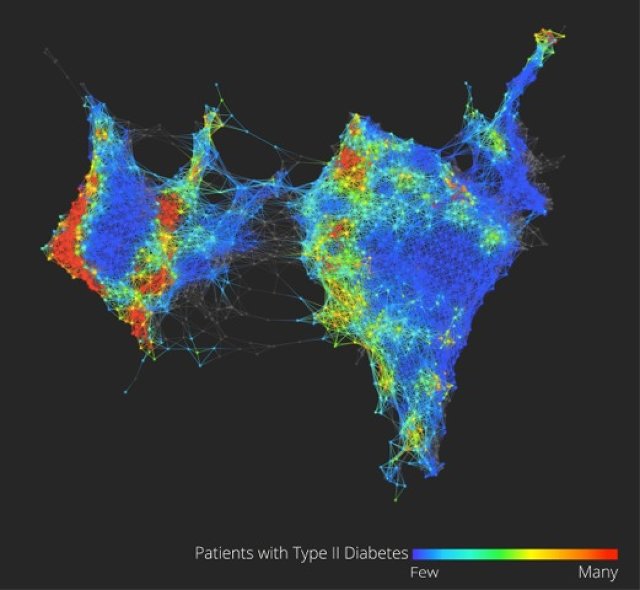
On it (see the figure above) is a visualization of the health data of 30,000 Sinai patients who have volunteered to share their information with researchers. He points out, in color, three separate clusters of the people who have Type 2 diabetes. What we’re looking at could be an entirely new notion of a highly scrutinized disease. “Why this is interesting is we could really be looking at Type 2, Type 3, and Type 4 diabetes,” says Dudley. “Right now, we have very coarse definitions of disease which are not very data-driven.” (Patients on the map are grouped by how closely related their health data is, based on clinical readings like blood sugar and cholesterol.)
From this map and others like it, Dudley might be able to pinpoint genes that are unique to diabetes patients in the different clusters, giving new ways to understand how our genes and environments are linked to disease, symptoms, and treatments. In another configuration of the map, Dudley shows how racial and ethnic genetic differences may define different patterns of a disease like diabetes–and ultimately, require different treatments.
These are just a handful of small examples of what could be done with more data on patients in one location, combined with the power to process it. In the same way Facebook shows the social network, this data set is the clinical network. (The eventual goal is to enroll 100,000 patients in what’s called the BioMe platform to explore the possibilities in having access to massive amounts of data.) “There’s nothing like that right now–where we have a sort of predictive modeling engine that’s built into a health care system,” Dudley says. “Those methods exist. The technology exists, and why we’re not using that for health care right now is kind of crazy.”
While Sinai’s goal is to use these methods to bring about more personalized diagnoses and treatments for a wide variety of diseases, such as cancer or diabetes, and improve patient care in the hospital, there are basic challenges that need to be overcome in order to making this vision achievable.
Almost every web company was born swimming in easily harvested and mined data about users, but in health care, the struggle has for a long time been more simple: get health records digitized and keep them private, but make them available to individual doctors, insurers, billing departments, and patients when they need them. There’s not even a hospital’s version of a search engine for all its data yet, says Hammerbacher, and in the state the slow-moving world of health care is in today, making predictions that would prevent disease could be just the icing on the cake. “Simply centralizing the data and making it easily available to a broad base of researchers and clinicians will be a powerful tool for developing new models that help us understand and treat disease,” he says.
Sinai is starting to put some of these ideas into clinical practice at the hospital. For example, in a hint of more personalized medicine that could come one day, the FDA is beginning to issue labels for some medicines that dictate different doses for patients who have a specific genetic variant (or perhaps explain that they should avoid the medicine altogether). The “Clipmerge” software that the hospital is beginning to now use makes it easier for doctors to quickly search and be notified of these kinds of potential interactions on an electronic medical record form.
On the prediction side, the hospital has already implemented a predictive model called PACT into its electronic medical record system. It is used to predict the likelihood that a discharged patient will come back to the hospital within 90 days (the new health care law creates financial incentives for hospitals to reduce their 90-day readmission rate). Based on the prediction, a high-risk patient at the medical center now might actually receive different care, such as being assigned post-care coordinator.
Eventually, there will be new kinds of data that can be put in mineable formats and linked to electronic patient records, from patient satisfaction surveys and doctors’ clinical notes to imaging data from MRI scans, Dudley says.
Right now, for example, the growing volumes of data generated from people’s fitness and health trackers is interesting on the surface, but it’s hard to glean anything meaningful for individuals. But when the data from thousands of people are mined for signals and links to health outcomes, Dudley says, it’s likely to prove valuable in understanding new ways to prevent disease or detect it at the earliest signs.
A major limitation to this vision is the hospital’s access to all of these new kinds of data. There are strict federal laws that govern patient privacy, which can make doctors loathe to experiment with ways to gather it or unleash it. And there are many hoops today to transferring patient data from one hospital or doctor to another, let alone from all the fitness trackers floating around. If patients start demanding more control over their own health data and voluntarily provide it to doctors, as Dudley believes patients will start to do, privacy could become a concern in ways people don’t expect or foresee today–just as it has on the Internet.
One thing is clear: As the health care system comes under pressure to cut costs and implement more preventative care, these ideas will become more relevant. Says Dudley: “A lot of people do research on computers, but I think what we’re hoping for is that we’re going to build a health care system where complex models … are firing on an almost day-to-day basis. As patients are getting information about them put in the electronic medical record system there will be this engine in the background.”
Upworthy, flow, dopamine…
This is actually about behaviour change, flow and dopamine… vulnerable, manipulable moments in conscious life being exploited by new online offerings like upworthy. Downloadable crack. Hope it starts being used more for good…
This Cat May Have Just Saved Canada. You Won’t Believe How.

Last Friday, Guelph resident Andrew McPherson’s cat, Tutu, appears to have achieved the impossible. Local residents claim their small town will never be the same again, and the future of Canada now seems certain.
Ok, so this article has nothing to do with a mystical cat or the sleepy suburb an hour outside of Toronto, but if you’re reading this, your curiosity was piqued. And there’s good reason.
Part of it is what is now dubbed the Upworthy-style headlines. Started in March 2012 by ex-employees of Move On and The Onion, the viral media site clocked an incredible 87 million unique visitors last month. The site’s headline aesthetic—a mini-story that makes clicking through irresistible—has been cloned by numerous websites attempting to create their own clickbait.
While The Atlantic’s Robinson Meyer recently explained the analyticsbehind the massive surge in Upworthy’s traffic, what is really interesting is why the titles are so seductive. It all has to do with our SEEKING system.
While not usually considered an emotional system in our brain, Estonian-born American neuroscientist Jak Panksepp argues that SEEKING is a function of the main instinctual-emotional system in humans in The Archaeology of Mind. We need to be in this mode in order to chase a romantic partner, find food, get to work in the morning…even get out of bed in the morning.
While such regular activities seem everyday, it is in this enormous neural pathway—from the midbrain to the Lateral hypothalamus into the medial frontal cortex—that dopamine is released. And without dopamine, we would have no motivation to do anything in life.
Yet what makes this system even more incredible is not that dopamine is released during gratification, but several seconds before we’re gratified. That is, while we’re engaged in seeking, our anticipation of an event—the first sip of beer, the moments before you undress a partner, the build up before the beat drops—forces dopamine to be released.
Relating this pathway to music, Ohio State university music researcherDavid Huron writes,
As we listen to music our anticipation builds, which generates pleasurable experiences for the listener. When a stimulus is anticipated, a positively-valenced emotional response arises.
This is why disappointment ensues if you’re expecting a beat to drop and it doesn’t—or if you click through an article about nationalistic Canadian cats to find out it has nothing to do with feline life.
The anticipation phase could also help explain the ‘magical’ experience one encounters when engaged in what Hungarian psychology professorMihály Csíkszentmihályi calls Flow: a runner’s high, being immersed in a novel, any moment when your complete and total reality is present in one focused effort.
When musicians, athletes, actors and chess players describe being in Flow experiences, they claim the impetus for action was not consciously initiated. Their movements seem to flow like a river with no consciousness of how they were moving or acting. Neuroscientist and author Sam Harrissays, “This experience has been at the core of human spirituality for millennia.”
The tiny squirts of dopamine we receive when hearing the ding of a text message or seeing a snazzy headline taps into that same anticipatory neural system. If the content matches our expectations, we feel satisfied, and depending on how much it blows us away—Zach Galifianakis Says Everything You Want to Say to Justin Bieber Right to His Face is one great example—we can then feel inspired, outraged and a whole host of other emotions. This is the brilliance of Upworthy: tapping into our ancient neural networks of anticipation and gratification.
Image: Renata Apanaviciene/shutterstock.com
Healthways…
http://www.healthways.com || http://www.healthways.com.au
Christian Sellars from MSD put on a terrific dinner in Crows Nest, inviting a group of interesting people to come meet with his team, with no agenda:
- Dr Paul Nicolarakis, former advisor to the Health Minister
- Dr Linda Swan, CEO Healthways
- Ian Corless, Business Development & Program Manager, Wentwest
- Dr Kevin Cheng, Project Lead Diabetes Care Project
- Dr Stephen Barnett, GP & University of Wollongong
- Warren Brooks, Customer Centricity Lead
- Brendan Price, Pricing Manager
- Wayne Sparks, I.T. Director
- Greg Lyubomirsky, Director, New Commercial Initiatives
- Christian Sellars, Director, Access
MSD are doing interesting things in health. In Christian’s words, they are trying to uncouple their future from pills.
After some chair swapping, I managed to sit across from Linda Swan from Healthways. It was terrific. She’s a Stephen Leeder disciple, spent time at MSD, would have been an actuary if she didn’t do medicine, and has been on a search that sounds similar to mine.
Healthways do data-driven, full-body, full-community wellness.
They’re getting $100M multi-years contracts from PHIs.
Amazingly, they’ve incorporated social determinants of health into their framework.
And even more amazingly, they’ve been given Iowa to make healthier.
They terraform communities – the whole lot.
Linda believes their most powerful intervention is a 20min evidence-based phone questionnaire administered to patients on returning home, similar to what Shane Solomon was rolling out at the HKHA. But they also supplant junk food sponsorship of sport and lobby for improvements to footpaths etc.
Just terrific. We’re catching up for coffee in January.
BMJ: Can behavioural economics make us healthy
- BE policies are by design less coercive and more effective than traditional approaches
- It is generally far more effective to punish than to reward
- Sticks masquerading as carrots – simultaneous, zero-sum incentives and penalties
- References to policies which have and have not worked – but why can’t policy be research?
- Conventional economics can therefore justify regulatory interventions, such as targeted taxes and subsidies, only in situations in which an individual’s actions imposes costs on others—for example, second hand cigarette smoke. But the potential reach of behavioural economics is much greater. By recognising the prevalence of less than perfectly rational behaviour, behavioural economics points to a large category of situations in which policy intervention might be justified—those characterised by costs which people impose on themselves (internalities), such as the long term health consequences of smoking on smokers.
- Is it fair to say that in a universal health care system, any preventable ill health imposes costs on others, as it is the tax payer who picks up the cost of treatment?
- present bias: the tendancy for decision makers tend to put too much weight on costs and benefits that are immediate and too little on those that are delayed. Present bias can be used to positive effect by providing small, frequent (i.e. immediate) payments for beneficial behaviours e.g. smoking cessation, medication adherence, weight loss
- “peanuts effect” decision error: the tendency to pay too little attention to the small but cumulative consequences of repeated decisions, such as the effect on weightof repeated consumption of sugared beverages or the cumulative health effect of smoking.
- competition and peer support are more powerful forms of behaviourally mediated interventions
Care of Nicholas Gruen.
PDF: CanBehaviouralEconomicsMakeUsHealthier_BMJ
Similarly in Health Affairs: http://content.healthaffairs.org/content/32/4/661.short
RWJF: How behaviour change really happens
From the video:
- don’t set up to fail: start with well motivated and capable people
- the only way to effect long lasting change is either via baby steps or change in the environment
- agile fast fail / rapid iteration R&D methodology (common in silicon valley) is something health doesn’t do, but should
How Behavior Change Really Happens
BJ Fogg, director of the Stanford Persuasive Technology Lab, is a social scientist, innovator, and teacher who creates systems to change behavior. “If we can help people understand how behavior change really happens in the long-term, then I believe people can design some of their own solutions to have healthier behaviors.” —BJ Fogg
If we want people to have healthy habits, we need to understand where these habits come from. BJ Fogg’s behavior model gives us a compelling understanding for how behavior change happens, and allows us to better see how our work could inspire these changes.”

Economist Intelligence Unit – Rethinking Cardiovascular Disease Prevention
Source: http://www.economistinsights.com/healthcare/opinion/heart-darkness%E2%80%94fighting-cvd-all-mind
CVD prevention at population level, such as a “fat tax” or smoking ban, relies heavily on regulation. This is its greatest strength – it can compel healthy behaviour (or seat belt wearing) – but also its greatest potential weakness. It inevitably involves some degree of coercion, which runs the risk of paternalism.It need not involve regulation, however. The same human flaws that are exploited by the food industry to persuade us to buy certain items at the check-out can also be used to persuade us to act in the interests of our own health. The current UK government is attempting to turn psychological weakness into an advantage outside of the legislative framework.
Its Behavioural Insights Team, commonly referred to as the “nudge unit”, is designed to seek “intelligent ways” to support and enable people to make better choices, using insights from behavioural science and medicine instead of increased rulemaking. Many of these goals overlap with CVD prevention, from smoking cessation to encouraging kids to eat healthier foods and walk to school more often. Early successes have brought them to the attention of the Obama administration in the US.
Besides the difficulties of making positive lifestyle changes, non-adherence to treatment is another significant obstacle to effective CVD prevention. Even after suffering a CVD incident, some patients forget to take their medication; other patients opt not to complete a course of treatment for other reasons, ranging from concerns about costs, the inconvenience involved with travel, to feelings of despondency caused by depression and anxiety. At its most anodyne, individuals frequently stop taking drugs prescribed for prevention after they feel better and think themselves cured.
This is part of a much wider medical problem: in the rich world adherence to treatment for all diseases is around 50%. Recognising the commercial opportunities here, private enterprise is looking to play a greater role. Earlier this year a US company called WellDoc launched a smartphone product aimed at giving type 2 diabetics better management of their treatment, through tailoured advice and motivational coaching. In the UK, meanwhile, a start-up calledImpact Health is developing a similar health psychology smartphone product to increase adherence to treatment among sufferers of Crohn’s disease.
CVD patients stand to benefit from such development in medical technology, although they may have to wait a little while yet. Impact Health’s online platform requires patients to have a smartphone. For this reason the start-up is targeting Crohn’s first and not CVD. As David Knull, one of its directors, explains, the profile of the average sufferer is generally around 30 years old—far younger than the average CVD patient, and much more likely to have a smartphone.
Report source: http://www.economistinsights.com/healthcare/analysis/heart-matter
Report PDF: The heart of the matter – Rethinking prevention of cardiovascular disease
The heart of the matter: Rethinking prevention of cardiovascular disease is an Economist Intelligence Unit report, sponsored by AstraZeneca. It investigates the health challenges posed by cardiovascular disease (CVD) in the developed and the developing world, and examines the need for a fresh look at prevention.
The report is also available to download in German, French, Italian, Spanish, Portuguese (Brazilian) and Mandarin—see the Multimedia tab
Why read this report
- Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the world’s leading killer. It accounted for 30% of deaths around the globe in 2010 at an estimated total economic cost of over US$850bn
- The common feature of the disease across the world is its disproportionate impact on individuals from lower socio-economic groups
- Prevention could greatly reduce the spread of CVD: reduced smoking rates, improved diets and other primary prevention efforts are responsible for at least half of the reduction in CVD in developed countries in recent decades…
- …but prevention is little used. Governments devote only a small proportion of health spending to prevention of diseases of any kind—typically 3% in developed countries
- Population-wide measures like smoking bans and “fat taxes” yield significant results but require political adeptness to succeed. There is no shortcut for the slow work of changing hearts and minds
- The size of the CVD epidemic is such that a doctor-centred health system will not be able to cope. Innovative ways for nurses and non-medical personnel to provide preventative services are needed
- A growing number of stakeholders are involved in CVD prevention, sharing the burden with governments. Now, greater collaboration across different sectors and interest groups should be encouraged
- Collaboration works when incentives of stakeholders are aligned, including business. Finland’s famed North Karelia project suggests better alignment of interests is crucial to a successful “multi-sectoral” approach
Cardiovascular disease is the dominant epidemic of the 21st century. Dr Srinath Reddy, president of the World Heart Federation
We know a lot about what needs to be done, it just doesn’t get done. Beatriz Champagne, executive director of the InterAmerican Heart Foundation
Action at the country level will decide the future of the cardiovascular epidemic. Dr Shanthi Mendis, director ad interim, management of non-communicable diseases, WHO
Living on the edge with Farzad
- It’s not as simple as you give people information and they change their behavior. It’s information tools that build on that data and build on communities and a much more sophisticated understanding about how behavior changes. What TEDMED is also great at, is understanding the power of marketing. People think of marketing of being about advertising, but marketing is the best knowledge we have about how to change behavior and all those intangibles, those predictably irrational insights, of how and why we do what we do.
- It’s harnessing those, instead of having them lead to worse health – like present value discounting that leads to people wanting to procrastinate and eat that doughnut now instead of going to the gym. Or the power of anchoring, where we fixate on the first thing we see and won’t think objectively about the true risks of things. Or the herd effect, our friend is overweight and so we are more likely to be overweight.
- All those nudges that are possible can be delivered to us ubiquitously and continuously, and we can choose to have them. It’s not some big brother dystopic vision. It’s me saying, ‘I want to be healthier, so I will do something now that will help me overcome and use my irrationality to help me stay healthy. To me, that’s the neat new edge between mobile cloud computing, personal healthcare, behavioral economics, healthcare IT, data science and visualization, design, and marketing. It’s that sphere that has so many possibilities to get us to better health.
http://blog.tedmed.com/?p=4153
The exit interview: Farzad Mostashari on imagination, building healthcare bridges and his biggest “aha” moments
 Farzad Mostashari, MD, stepped down from his post as the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology at the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), during the first week of October, which was also the first week of the Federal partial shutdown. During his tenure, Dr. Mostashari, who spoke at TEDMED 2011 with Aneesh Chopra, led the creation and definition of meaningful use incentives and tenaciously challenged health care leaders and patients to leverage data in ways to encourage partnerships with patients within the clinical health care team.
Farzad Mostashari, MD, stepped down from his post as the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology at the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), during the first week of October, which was also the first week of the Federal partial shutdown. During his tenure, Dr. Mostashari, who spoke at TEDMED 2011 with Aneesh Chopra, led the creation and definition of meaningful use incentives and tenaciously challenged health care leaders and patients to leverage data in ways to encourage partnerships with patients within the clinical health care team.
Whitney Zatzkin and Stacy Lu had the opportunity to speak with Dr. Mostashari during his last week in office.
WZ: Sometimes, a person will experience an “aha!” moment – a snapshot or event that reveals a new opportunity and challenges him/her to pursue something nontraditional. Was there a critical turning point when you figured out, ‘I’m the guy who should be doing this?’
Yeah, I’ve been fortunate to have a couple of those ‘aha’ moments in my life. One of them was when I was an epidemic intelligence service officer back in 1998, working for the CDC in New York City. I’ve always been interested in edge issues, border issues; things that are on the boundaries between different fields. I was there in public health, but I was interested in what was happening in the rest of the world around electronic transactions and using data in a more agile way.
In disease surveillance we often look back — the way we do claims data now – years later or months later you get the reports and you look for the outbreak, and often times the outbreak’s already come and gone by the time you pick it up. But I started thinking and imagining: What if the second something happens, you can start monitoring it? In New York City the fire department was monitoring ambulance calls. I said, ‘Wow, if we could just categorize those by the type of call, maybe we’ll see some sort of signal in the noise there.’
When I was first able to visualize the trends in the proportion of ambulance dispatches in NYC that were due to respiratory distress, what I saw was flu. What jumped out at me was the sinusoidal curve. Wham! At different times of year, it could be a stutter process – it would go up and you would see this huge increase, followed two weeks later by an increase in deaths. It was like the sky opening up. The evidence was there all along, but I am the first human being on earth to see this. That was validation, for me, of the idea that electronic data opens up worlds. To bring that data to life, to be able to extract meaning from those zeros and ones — that’s life and death. That was my first ‘aha’ moment.
The second aha was after I joined New York City Department of Health, and I started a data shop to build our policy around smoking and tracking chronic diseases. What we realized was that healthcare was leaving lives on the table. There were a lot of lives we could save by doing basic stuff a third-year medical student should do, but we’re not doing it. Related to that – Tom Frieden had a great TEDMED talk about everybody counts.
I said, ‘I want to take six months off and do a sabbatical, and see if there’s anything to using electronic health records to provide those insights, not to save lives by city level, but on the 10 to the 3 level – the 1,000 patient practice. That started the whole journey. None of the vendors at the time had the vision we had, but we finally got someone to work with us and rolled this system out. We called some doctors some 23 times, and did all the work to get to the starting line. Finally, I took Tom on a field visit to see one of the first docs to get the program.
It was a very normal storefront in Harlem, and a nice physician, very caring, very typical. I asked her what she thought of the program. She said, ‘It’s ok. I’m still getting used to it.’ I said, ‘Did you ever look at the registry tab on the right, where you can make a list of your patients? She said no. I said, ok – how many of your elderly patients did you vaccinate for flu this year? She said, ‘I don’t know, about 80 to 85 percent. I’m pretty good at that.’ I said, ‘o.k., let’s run a query.’ And it was actually something like 22 percent. And she said – this was the aha moment – ‘That’s not right.’
That’s generally the feeling the docs have when they get a quality measure report from the health plan. But that’s population health management — the ability to see for the first time ever that everybody counts. And being able to then think about decision support and care protocols to reduce your defect rate. That was the validation that we’re on to something. Without the tools to do this, all the payment changes in the world can’t make healthcare accountable for cost and quality if you can’t see it.
WZ: Everyone has that moment in life when they’re considering all of their career options. As you were considering medical school, what else was on the table?
I actually didn’t think I was going to go to medical school. I was at the Harvard School of Public Health. I was interested in making an impact in public health. I grew up in Iran, and thought I would do international public health work. And then my dad got sick; he had a cardiac issue. The contrast between the immediacy of the laying on of hands of healthcare, and the somewhat abstractness of international public health — the distance, the remove — tipped me into saying, ‘You know, maybe I should go to medical school.’ I’ve been on that edge between healthcare and public health ever since, and always trying to drag the two closer to each other.
SL: Fast forward 20 years. You’re giving another talk at TEDMED. What’s the topic?
TEDMED and Jay Walker’s vision is more powerful in the futurescope, rather than in the retroscope. It’s more powerful to be where we are today and imagine a different future rather than look back and say, ‘Oh, yeah, we’ve done this.’ So what’s the future I would love to imagine?
The most exciting thing – as Jay Walker once mentioned in a talk comparing “medspeed” to “techspeed” – is to fully imagine what will happen if techspeed is brought to healthcare. Right now, there’s all this unrealized value that’s being given away for free that doesn’t show up on any GDP lists – what Tim O’Reilly called “the clothesline paradox.” That kind of possibility brought to medicine, but where software costs $100,000 as opposed to free, and it evolves daily and is more powerful and quicker every day, and it’s beautiful and usable and intuitive, and that’s what people compete on.
And all of that is toward the goal of empowering people. Someone said, maybe it was Jay at TEDMED, that a 14-year-old kid in Africa with a smart phone has more access to information than Bill Clinton did as President. Information is power, and it has changed everything but healthcare. For me the vision is breaking down that wall, so that patients can be empowered and can bind themselves to the mast to use what we’ve learned about how behavior changes.
It’s not as simple as you give people information and they change their behavior. It’s information tools that build on that data and build on communities and a much more sophisticated understanding about how behavior changes. What TEDMED is also great at, is understanding the power of marketing. People think of marketing of being about advertising, but marketing is the best knowledge we have about how to change behavior and all those intangibles, those predictably irrational insights, of how and why we do what we do.
It’s harnessing those, instead of having them lead to worse health – like present value discounting that leads to people wanting to procrastinate and eat that doughnut now instead of going to the gym. Or the power of anchoring, where we fixate on the first thing we see and won’t think objectively about the true risks of things. Or the herd effect, our friend is overweight and so we are more likely to be overweight.
All those nudges that are possible can be delivered to us ubiquitously and continuously, and we can choose to have them. It’s not some big brother dystopic vision. It’s me saying, ‘I want to be healthier, so I will do something now that will help me overcome and use my irrationality to help me stay healthy. To me, that’s the neat new edge between mobile cloud computing, personal healthcare, behavioral economics, healthcare IT, data science and visualization, design, and marketing. It’s that sphere that has so many possibilities to get us to better health.
The thing about the health is, we have a Persian saying: Health is a crown on the head of the healthy that only the sick can see. When you have it, you don’t appreciate it, but when you’re sick and someone you love is sick, there’s nothing better. You would do anything to get that. We need to bring that vision of the crown to everyone and help each of us grab it when we can.
WZ: I noticed you closing your eyes while preparing to answer a question. How do you pursue being able to exercise your imagination, in particular while you’re sitting in a building that’s been marked for being the least imaginative?
Because the world, as it is, is too immediate and real and limiting, sometimes you have to close your eyes to see a different world.
What has been amazing has been to see that, contrary to what people expect, this building is filled with people with untapped, unbound, unfettered imaginations who are slogging through. They’re just trapped. You give them the opening, the smallest bit of daylight to exercise that, and they’re off and running.
I give a lot of credit to Todd Park as our “innovation fellow zero,” He saw the possibility that there are more than two kinds of people in the world, innovators and everybody else. For him, it was about going to create a space where outside innovators can be the catalyst or spark that elevates and permissions the innovation of the career civil servant at CMS in Baltimore. That’s been cool.
SL: What’s your bowtie going to do after you leave HHS? Will we see it lounging on the beach in Boca?
I like the bowtie. I think I’m going to keep it. Perhaps the @FarzadsBowtie Twitter handle is going to go into hibernation, I don’t know. I don’t control it. One of the things the bowtie does for me is help me remember not to get too comfortable.
I once said at the Consumer Health IT Summit – ‘You’re a bunch of misfits – glorious misfits. And I feel like I’m very well suited to be your leader. You know, I always felt American in Iran, and felt Iranian in America when I came here. I felt like a jock among my geeky friends, and like a geek among jocks. For crying out loud, I wear a bowtie! I don’t have to tell you I’m a misfit.’
It’s that sense of not fitting into the world as it is. The world doesn’t fit me. So instead of saying, ‘I need to change,’ this group of people said, ‘The world needs to change.’ That’s the difference between a misfit and a glorious misfit.
The person who doesn’t fit into our healthcare system is the patient. The patient’s preferences don’t fit into the need to maximize revenue and do more procedures. The patient’s family doesn’t fit into the, ‘I want to do an eight-minute visit and get you out the door’ agenda. The patient asking questions doesn’t fit. That’s the change we need to make. It’s not that we need to change. Healthcare needs to change to fit the patient.
Shortly following this interview, Dr. Mostashari left HHS and is now the a visiting fellow of the Engelberg Center for Health Care Reform at the Brookings Institution, where he aims to help clinicians improve care and patient health through health IT, focusing on small practices.
This interview was edited for length and readability.
